3D Bioprinting
May 16, 2021 | 4 min read

May 16, 2021 | 4 min read

There are hundreds of people on organ transplant lists waiting for critical organs to save their lives. Unfortunately, the demand for organs does not meet the number of organ donors. What if this crisis could be resolved with new organs synthesized in vitro. This idea leads to the evolutionary concept of 3D Bioprinting.
3D Bioprinting is a mind-boggling technology that emerged in the 21st century. It is a branch of regenerative medicine currently under development. 3D bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other biocompatible materials to print living structures layer-by-layer, mimicking natural living systems. The technology uses a material known as bioink to create these biological structures. The technique is widely applicable in medicine and bioengineering, specifically on drug validations and organ transplantations.
The process has complex steps involved as it requires high precision.The critical steps in this technique can be summarised into:
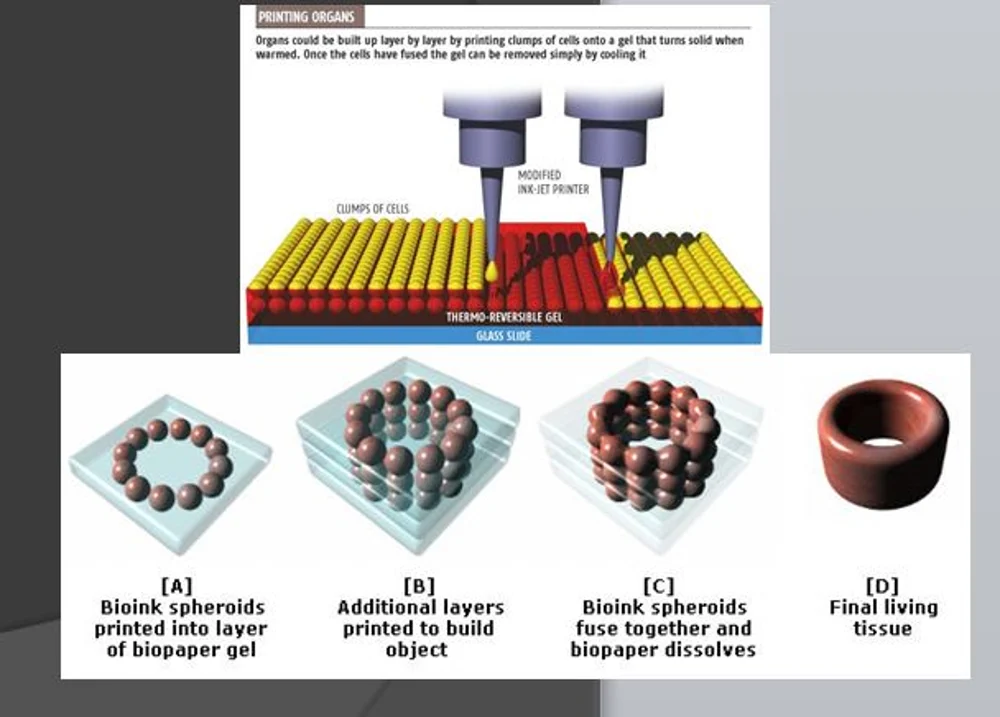
Figure 1. The Art of Bioprinting
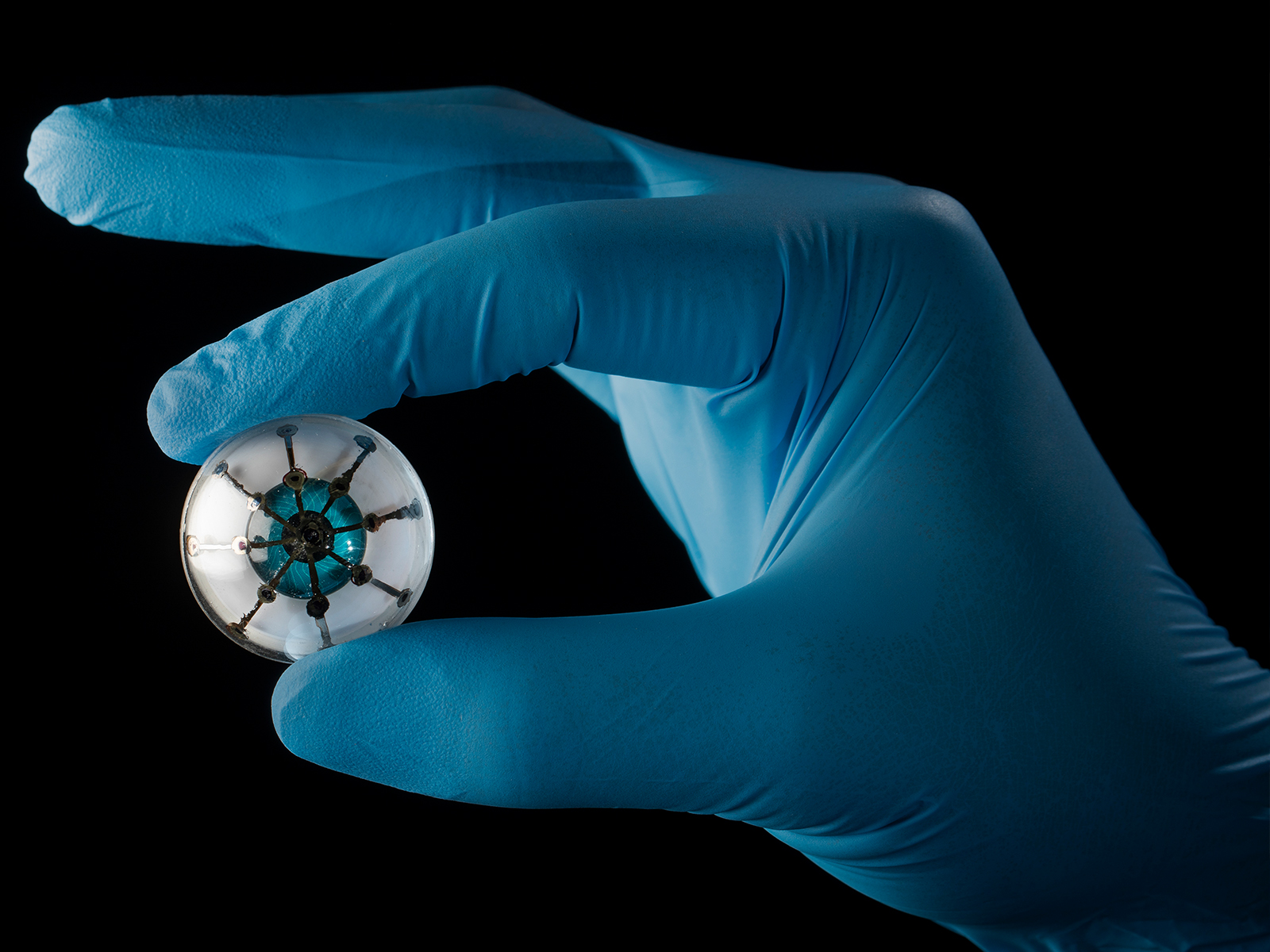
Figure 2. Bionic Eye
Figure 3. Bioprinter