Sanger Sequencing
Oct 16, 2020 | 3 min read
Oct 16, 2020 | 3 min read

Sanger sequencing, also known as the chain termination method, is used to determine the nucleotide sequence of the molecule. This method was developed by the Nobel Laureate Frederick Sanger and his team in 1977.
The main steps in this process include:
The DNA sequence for Chain termination PCR:
The desired DNA sequence is used as the template for the chain termination PCR, which includes modified nucleotides called dideoxyribonucleotides (ddNTPs). In chain termination PCR, it uses both ddNTPs and dNTPs. Since ddNTP lacks the
3’-OH group required for phosphodiester bond formation, therefore when the DNA Polymerase incorporates ddNTP, the extension ceases. As a result, this produces many copies of the oligonucleotide with the DNA sequence of interest, at random lengths.
Size Separation by Gel Electrophoresis:
The obtained oligonucleotide is then separated according to size using gel electrophoresis. The principle of gel electrophoresis is that the negatively charged DNA sample, when subjected to an electric current, moves from one end of the
gel matrix to the positive electrode and the speed at which the DNA sample moves through the matrix, depends on the size, causing their separation. So when the oligonucleotide is loaded into the gel matrix and run, it will get arranged
from largest to smallest fragment, when the gel is read from bottom to top.
Gel Analysis and determination of DNA sequence:
This step involves reading the gel to determine the sequence of the DNA. This is possible since the DNA Polymerase works from a 5’ to 3’ direction starting with the primer and each terminal ends with a corresponding ddNTP. The band is
then read from smallest to largest (because the shortest fragment would terminate first from the 5’ end and so on) helping us determine the 5’ to 3’ sequence of the DNA template.
Usually, a chromatogram is used to figure out the sequence. This identifies the sequence with the use of ddNTP, which has fluorescent tags. Each sequence is recognized by the fluorescent tag of the terminal ddNTP. More importantly,
the four ddNTPs are tagged with different fluorescent tags so that they can be directly tied to the identity of the terminal ddNTP. Thus the chromatogram shows the fluorescent peak of each nucleotide sequence along with the length
of the DNA template.
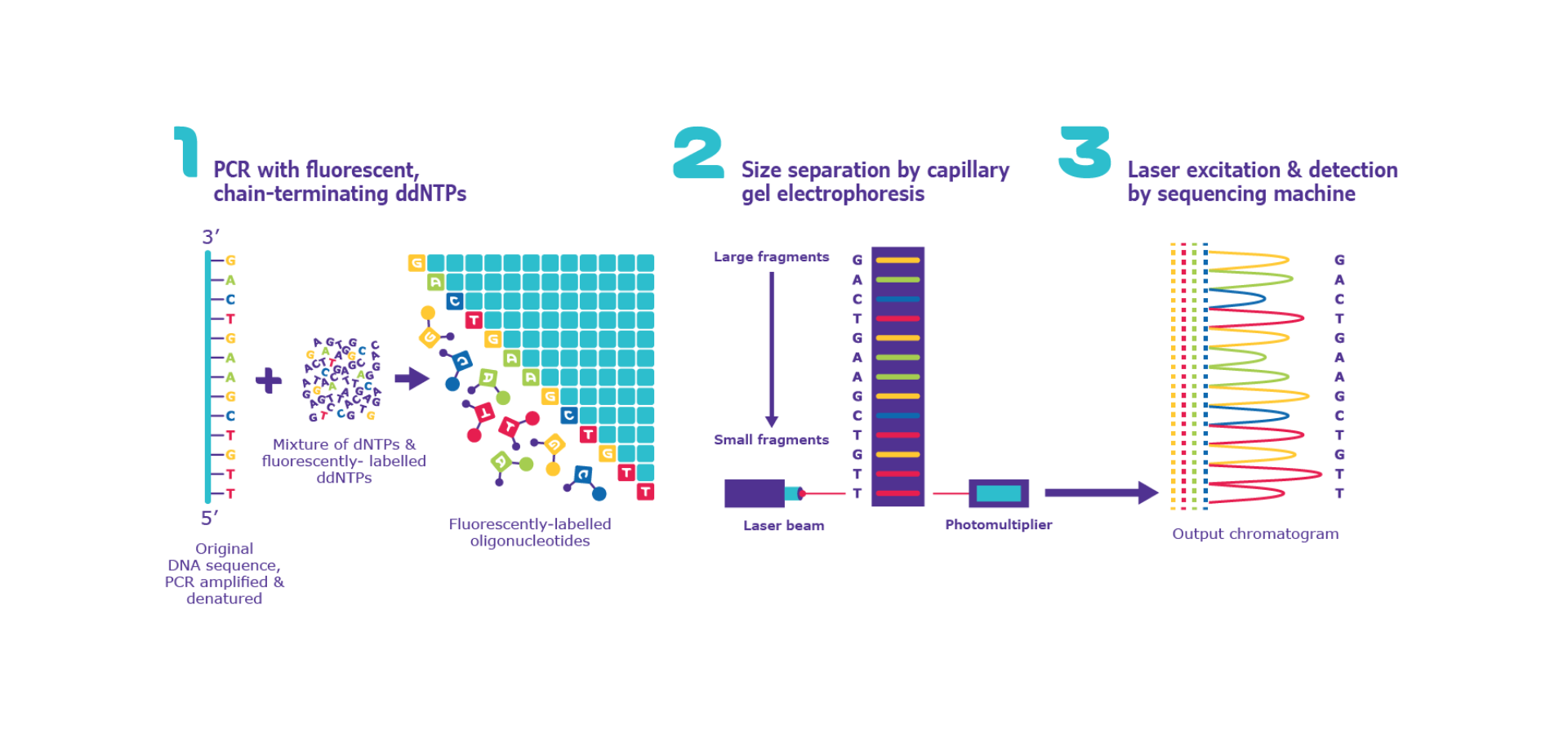
Figure 1. Sanger Sequencing process schematic. Here, we see the three main steps of Sanger sequencing, namely, formation of frgaments with fluorescent ddNTPs, fragment separation by size and detection by a Sequencing machine.

Figure 2. The famous boy band Backstreet Boys released their album DNA in 2019, with one of their cover page having the background of the Sanger Sequencing.